Nepal has achieved significant development progress in recent decades. To sustain the development gains, Nepal must adapt its development pathway to a changing climate. Nepal 's Country Climate and Development Report (CCDR) identifies ways that Nepal can achieve its overall development objectives while fostering its strategic ambition to transition to a greener, more resilient, and inclusive development pathway.
Global warming and climate change are already affecting Nepal��s gross domestic product. Increased flooding, heat stress on labor productivity and health, and heat stress on crops and livestock are expected to be a continual drag on growth. Women, indigenous people, and other marginalized groups are often excluded from mainstream development and suffer from cumulative and cascading impacts of climate change and disasters. Without comprehensive and scaled-up climate action, climate change will continue to jeopardize gains in Nepal��s human development and poverty reduction.
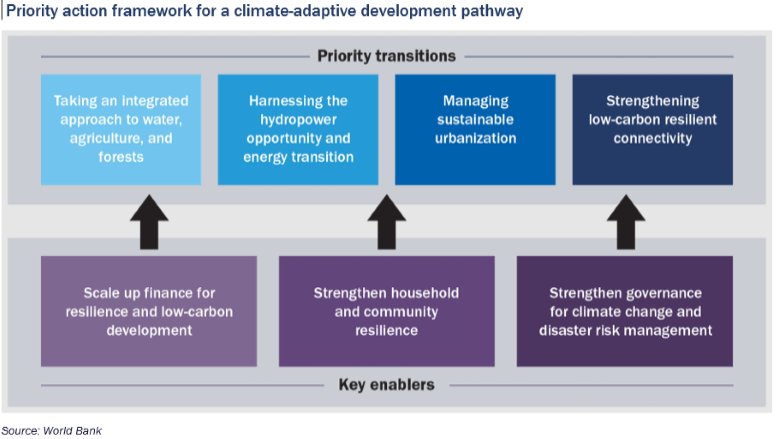
To respond to this challenge, Nepal is already implementing steps to recalibrate its economy by adopting a Green, Resilient, and Inclusive Development (GRID) approach. In 2021, Nepal adopted the Green, Resilient and Inclusive Development (GRID) approach as a national vision to guide long-term green growth and build resilience to climate and other shocks that are barriers to Nepal��s development ambitions. Under Nepal��s federal structure, the local governments are placed at the center of climate resilience and development efforts with extensive implementation responsibilities and play a crucial role in translating the GRID strategy into action.
Nepal has pledged to achieve net zero emissions by 2045 and to significantly scale up hydropower investment in the coming decade. Nepal has begun to put in place the necessary policy framework, such as the 2019 National Climate Change Policy, the 2022 Solid Waste Management Policy, the 2022 Forest Regulation and the 2022 Land Use Regulation. However, implementation of this reform agenda and prioritization of investments is incipient. Moreover, enhanced prioritization and efficiency of public expenditure are required to maximize climate and development benefits.
Last Updated: Sep 15, 2022